 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
BGP Connection Establishment: Open Messages
(Page 2 of 2)
BGP Open Message Format
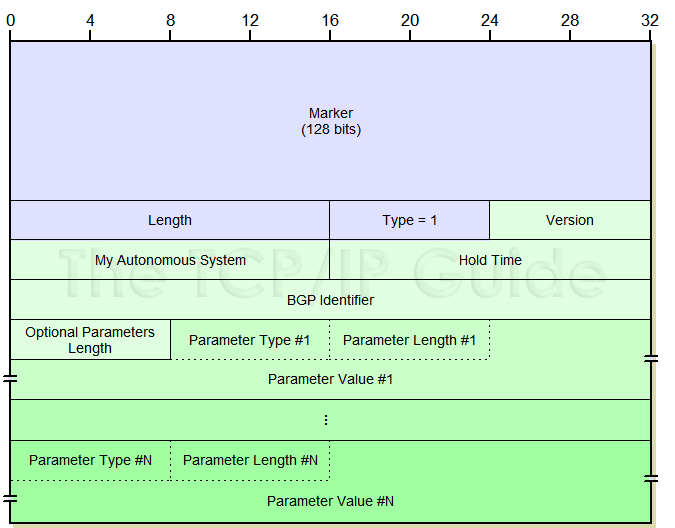
The specific format for BGP Open messages can be found in Table 137 and Figure 193.
Field Name |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Marker |
16 |
Marker: This large field at the start of each BGP message is used for synchronization and authentication. See the discussion of the BGP general message format for details. |
Length |
2 |
Length: The total length of the message in bytes, including the fields of the header. Open messages are variable in length. |
Type |
1 |
Type: BGP message type, value is 1 for Open messages. |
Version |
1 |
Version: Indicates the BGP version the sender of the Open message is using. This field allows devices to reject connections with devices using versions they may not be capable of understanding. The current value is 4, for BGP-4, and is used by most, if not all, current BGP implementations. |
My Autonomous System |
2 |
My Autonomous System: Identifies the autonomous system number of the sender of the Open message. AS numbers are centrally managed across the Internet in a manner similar to how IP addresses are administered. |
Hold Time |
2 |
Hold
Time: The number of seconds that this device proposes to use
for the BGP hold timer, which specifies how long a BGP peer will allow
the connection to be left silent between receipt of BGP messages. A
BGP device may refuse a connection if it doesn't like the value that
its peer is suggesting; usually, however, the two devices agree to use
the smaller of the values suggested by each device. |
BGP Identifier |
4 |
BGP Identifier: Identifies the specific BGP speaker. Recall that IP addresses are associated with interfaces, not devices, so each router will have at least two IP addresses. Normally the BGP identifier is chosen as one of these addresses. Once chosen, this identifier is used for all BGP communications with BGP peers. This includes BGP peers on the interface from which the identifier was chosen, and also BGP peers on other interfaces as well. So, if a BGP speaker with two interfaces has addresses IP1 and IP2, it will choose one as its identifier and use it on both of its interfaces. |
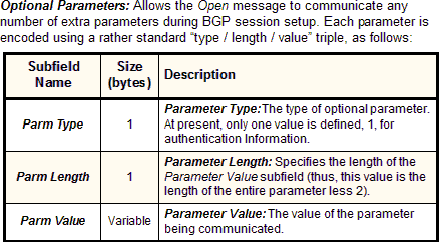
Opt Parm Len |
1 |
Optional Parameters Length: The number of bytes used for Optional Parameters (see below). If 0, no optional parameters are in this message. |
Optional Parameters |
Variable |
|
BGP Open messages currently use only one optional parameter: Authentication Information. Its Parameter Value subfield contains a one-byte Authentication Code sub-subfield, which specifies the type of authentication a device wishes to use. Following this is a variable-length Authentication Data sub-subfield. The Authentication Code specifies how authentication is to be performed, including the meaning of the Authentication Data field, and the manner in which Marker fields are to be calculated.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: BGP sessions begin with each peer in a connection sending the other a BGP Open message. The purpose of this message is to establish contact between devices, identify the sender of the message and its autonomous system, and negotiate important parameters that dictate how the session will be conducted.
Key Concept: BGP sessions begin with each peer in a connection sending the other a BGP Open message. The purpose of this message is to establish contact between devices, identify the sender of the message and its autonomous system, and negotiate important parameters that dictate how the session will be conducted.