 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IPv6 Datagram Extension Headers
(Page 2 of 6)
IPv6 Header Chaining Using the Next Header Field
The only field common to all extension header types is the Next Header field (which actually appears at the end of one header type, the ESP header). The 8-bit Next Header field is used to logically link all the headers in an IPv6 datagram as follows:
- The Next Header field in the main header
contains a reference number for the first extension header type.
- The Next Header field in the first extension
header contains the number of the second extension header type, if there
is a second one. If there's a third, the second header's Next Header
points to it, and so on.
- The Next Header field of the last extension header contains the protocol number of the encapsulated higher-layer protocol. In essence, this field points to the “next header” within the payload itself.
For example, suppose a datagram that encapsulates TCP has a Hop-By-Hop Options extension header and a Fragment extension header. Then, the Next Header fields of these headers would contain the following values:
- The main header would have a Next Header
value of 0, indicating the Hop-By-Hop Options header.
- The Hop-By-Hop Options header would have
a Next Header value of 44 (decimal), the value for the Fragment
extension header.
- The Fragment header would have a Next Header value of 6.
This is illustrated in Figure 106.
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







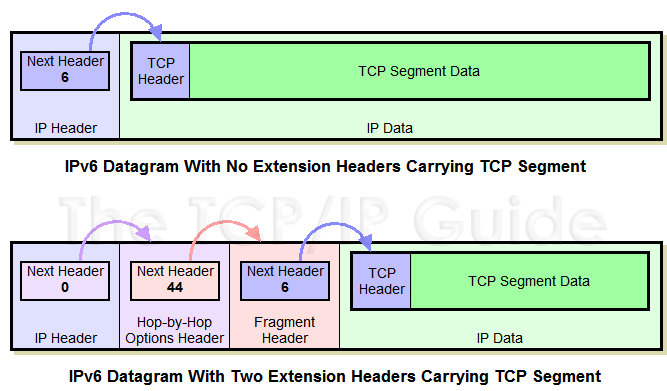
 Key Concept: The IPv6 Next Header field is used to “chain together” the headers in an IPv6 datagram. The Next Header field in the main header contains the number of the first extension header; its Next Header contains the number of the second, and so forth. The last header in the datagram contains the number of the encapsulated protocol that begins the Data field.
Key Concept: The IPv6 Next Header field is used to “chain together” the headers in an IPv6 datagram. The Next Header field in the main header contains the number of the first extension header; its Next Header contains the number of the second, and so forth. The last header in the datagram contains the number of the encapsulated protocol that begins the Data field.