 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IPv6 Datagram Options
(Page 2 of 2)
IPv6 Option Format
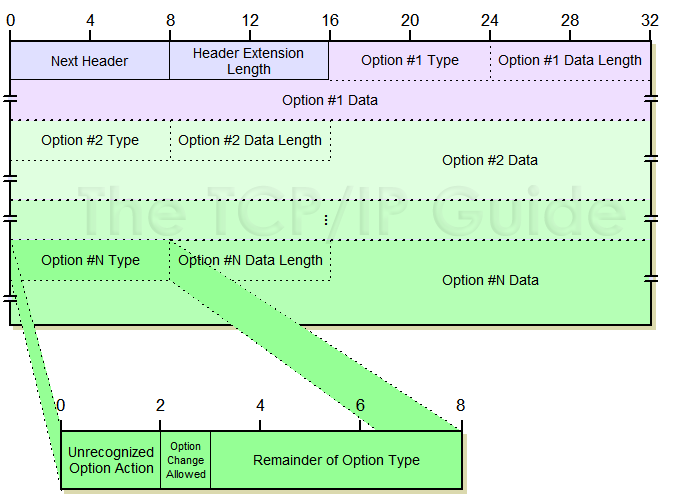
Each of these header types has a one-byte Next Header field, and a one-byte Header Extension Length field that indicates the header’s overall length. The rest of the header has one or more option fields. Figure 109 illustrates the overall format of these two headers. The format of each option is similar to that of IPv4 options, and is shown in Table 73.
|
Subfield Name |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Option Type |
1 |
|
Opt Data Len |
1 |
Option Data Length: Specifies the length of the Option Data subfield below. Note that this is a change in semantics from IPv4, where the length field indicated the size of the entire option; in IPv6 the length of the Option Type and Option Data Length fields are not included. |
Option Data |
Variable |
Option Data: The data to be sent as part of the option, which is specific to the option type. Also sometimes referred to as the Option Value. |
|
Since each option has a subfield for type, length and value (data), they are sometimes said to be TLV-encoded. If there are multiple options, they are placed one after each other in the header. At the end of all the options in a Hop-By-Hop Options or Destination Options extension header, padding may be placed to ensure that the header is a multiple of 8 bytes in length.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







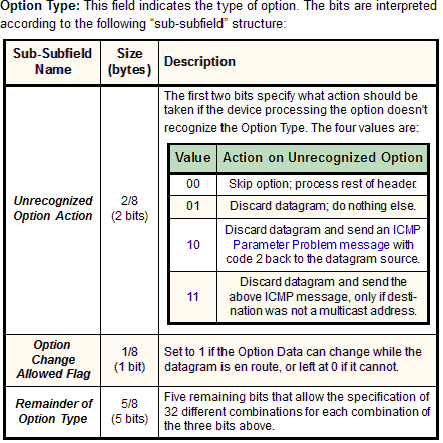
 Note: The Option Type subfield is a bit strange in terms of how it is interpreted. Even though it has a substructure with three sub-subfields as shown in
Note: The Option Type subfield is a bit strange in terms of how it is interpreted. Even though it has a substructure with three sub-subfields as shown in  Key Concept: Two IPv6 extension header types, Hop-By-Hop Options and Destination Options, are used to carry arbitrary optional information in IPv6 datagrams. Each consists of a set of variable-length options that are defined using three subfields indicating the option’s type, length and value.
Key Concept: Two IPv6 extension header types, Hop-By-Hop Options and Destination Options, are used to carry arbitrary optional information in IPv6 datagrams. Each consists of a set of variable-length options that are defined using three subfields indicating the option’s type, length and value.